Launch Your Foods, Cosmetics, NHPs, & Pet Products on Amazon Canada: Compliance FAQs
We understand the impact of changing Amazon Canada regulations on your business – and how non-compliance can hurt you. Q: But what does “non-compliance” even mean? Answer: It could be a lot of things: Mislead info: Your product descriptions need to be more accurate or include important details required by regulations body. Wrong or Restricted
... Read moreFDA Regulates Lab-Developed Tests for Safety

FDA (U.S) has recently revised its regulatory framework for laboratory-developed tests (LDTs). These in vitro diagnostic products (IVDs) are critical for analyzing substances such as proteins and DNA from human specimens like blood and tissue, playing a crucial role in diagnosing & monitoring health. Why this Matters LDTs are fundamental in facilitating healthcare decisions,
... Read moreFDA Facility Registration & Renewals (FDA Medical Device, Food & Drugs)

Quality Smart Solutions offers the best FDA Facility Renewal & Registration services in North America for Medical Devices, Food, and Drug FDA domestic and foreign facilities! With the facility renewal period fast approaching we’re going to touch upon the FDA Facility Registration and Renewal process for domestic/foreign medical devices, food, and drug facilities. We’ll outline
... Read moreDemystifying the Medical Device Regulatory Process: A guide for manufacturers
Navigating the complex medical device regulatory process can often feel like decoding a cryptic language. Manufacturers grapple with an intricate web of requirements, standards, and timelines while striving to bring life-saving innovations to market. But fear not! This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the medical device regulatory process and empower manufacturers with the knowledge and
... Read moreEverything to know about the GRAS Generally Recognized as Safe Database

Food manufacturers everywhere are willing to jump through hurdles to receive their GRAS Notifications and access to the generally recognized as safe database. In our past blogs, we’ve tackled the GRAS Notice, GRAS Ingredients, GRAS regulations, benefits of self-affirmed GRAS, GRAS Status, GRAS list for food additives, GRAS process, and More. Now that the benefits
... Read moreUS Cosmetic Regulatory Requirements for Manufacturers (MoCRA Regulations)

https://youtu.be/uuXA8yHrrZc Introduction: Behold the “Modernization of Cosmetic Regulation Act of 2022” that President Biden signed on December 29, 2022. This law requires an increased FDA oversight of cosmetics and their ingredients. In this article, we’ll discuss the key provisions, timelines for enforcement actions, and new requirements and summarize the regulatory implementation mentioned in this Act.
... Read moreEverything you should know about the registration and listing of Cosmetic Product Facilities and Products

This guidance provides suggestions and instructions to assist in submitting cosmetic product facility registrations and product listings to the FDA. It describes the FDA’s current thoughts and is only final if regulatory requirements are mentioned. This guidance document explains, among other things: •The statutory requirement to submit cosmetic product facility registrations and product listings; •Who is responsible
... Read moreNavigating the process: your guide to obtaining a Natural Health Product License

Are you looking to bring your natural health product to market? Navigating the process of obtaining a license can be daunting, but fear not – we’re here to guide you every step of the way. This comprehensive guide walks you through the intricacies of obtaining a natural health product license, ensuring you have the knowledge
... Read moreNavigating the regulatory landscape: Understanding the Importance of a Generally Recognized as Safe Database

In today’s rapidly evolving regulatory landscape, businesses face many challenges regarding ensuring compliance and product safety. One crucial aspect often overlooked is the importance of a Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) database. This database is a valuable resource for manufacturers and regulators, providing a comprehensive list of substances considered safe for use in food and
... Read moreHow to Secure a Natural Product Number in Canada

Are you a health and wellness entrepreneur looking to bring your products to the Canadian market? Navigating the Health Canada Natural Product Number (NPN) process can seem daunting, but fear not – we’re here to guide you every step of the way. In this comprehensive step-by-step guide, we’ll break down the entire NPN process, from
... Read moreBreaking Ground: How to open a drug testing facility FDA Facility Registration

Opening a drug testing facility can be a rewarding opportunity especially as demand for workplace and healthcare-related testing continues to grow. But before you begin, one step is absolutely essential: FDA facility registration. It confirms your compliance, protects your credibility, and ensures the accuracy of your testing services. This guide breaks the process down into
... Read moreWhy is Drug Establishment Registration (DEL) crucial?

In the dynamic and ever-evolving world of pharmaceuticals, ensuring compliance with FDA regulations is paramount. One crucial aspect that must be considered is drug establishment registration. This process plays a pivotal role in maintaining the safety and efficacy of drugs available in the market. This comprehensive guide will delve into everything you need to know
... Read moreDecoding the Jargon: Medical Device approvals 510(K) V.S. PMA differences & process
Are you a medical professional or someone involved in the healthcare industry? If so, you’ve likely come across the terms 510(k) and PMA regarding medical devices. But what do these terms mean, and why are they important? This article will decode the jargon and help you understand the critical differences between 510(k) and PMA.
... Read moreFood changed Forever? How EFSA Novel Foods are Revolutionizing the Industry

In a world where culinary boundaries are constantly expanding, the future of food holds endless possibilities. Enter EFSA Novel Foods, a revolutionary concept reshaping the food industry as we know it. From lab-grown meats to insect-based protein alternatives, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is paving the way for a new era of sustainable, innovative,
... Read moreFrom customs clearance to delivery: How USA Import Services can benefit your supply chain

In today’s global economy, businesses increasingly use international trade to source materials and sell products. However, the complex regulations and logistics involved in importing can create significant challenges for companies looking to expand their supply chains. That’s where USA import services come in. By providing comprehensive support from customs clearance to delivery, these services
... Read moreWhy is Quality Assurance important in Clinical Trials?

Introduction: Quality assurance is an essential part of clinical trials. It involves a set of processes that ensure that the study is conducted in compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards. These processes include study design, protocol development, data collection, analysis, and reporting. Quality assurance is critical to the success of clinical trials because it
... Read moreNHPs considered a therapeutic drug product under Vanessa’s Law

Introduction: Health Canada’s new dietary supplement regulations, which are intended to revamp an already successful system, are unintentionally harming both Canadian consumers, merchants, and brands as well as U.S. suppliers. Natural health products (NHPs) will be subject to the Protecting Canadians from Unsafe Drugs Act (Vanessa’s Law) authority as of June 22, 2023. This is so because
... Read moreMaximizing Results: How Clinical Trial Services support your research

As a researcher, you know that the success of your study depends on many factors, from the quality of your data to the effectiveness of your methods. One critical element that can greatly impact the outcome of your research is the clinical trial services you choose. Effective clinical trial services can help you maximize results
... Read moreThe benefits of having a Preventive Control Plan in place and how to maintain it
As the saying goes, prevention is always better than a cure. This is particularly true regarding food safety in the food industry. A preventive control plan is one of the most effective ways to ensure your products are safe for consumption. A preventive control plan is a written document outlining a food facility’s steps to
... Read moreWhy a Self-Affirmed GRAS Dossier Can Give Your Business an Edge

As a company developing new products, ensuring they are safe for consumption is essential. One way to achieve this is by obtaining a self-affirmed Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) dossier. This document provides evidence that the ingredients in your product are safe and do not require further testing. In comparison, it may seem unnecessary, but
... Read moreNavigating Safe Food for Canadians Regulations: What you should know

Food safety is a top priority for Canadians. With so many potential hazards lurking in our food supply, it’s more important than ever to be aware of the regulations to protect ourselves and our families. Enter the Safe Food for Canadians Regulations (SFCR), a comprehensive set of rules designed to ensure that all food sold
... Read moreBuilding trust & credibility in your food business with a FSVP Certificate

Consumers today are more careful about the food they buy.They want to know their food is safe, high quality, and compliant with regulations. This is where the Food Safety Verification Program (FSVP) certification becomes important.FSVP certification helps food businesses meet food safety rules set by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Building trust and
... Read moreEverything your Importer should do to ensure compliance and a smooth customs clearance

https://youtu.be/mWaBQzsa1_M Introduction In the world of international trade, importers of record play a crucial role in ensuring smooth customs clearance and maintaining compliance with various regulations. These key responsibilities require a deep understanding of import processes, documentation, and trade laws. From managing import licenses to accurately classifying products, importers of record are the linchpin that
... Read moreWhy NDC Numbers are vital for pharmaceutical companies?
https://youtu.be/cct8v4aXvhc In the fast-paced and ever-evolving world of pharmaceuticals, staying ahead of the competition is crucial. And one vital tool that can help pharmaceutical companies gain a competitive edge is the National Drug Code (NDC) number. These unique identifiers are a critical link between medications, manufacturers, and healthcare providers. In this digital age, where information
... Read moreFrom Hazard Analysis to Critical Control Points: A Deep Dive into the HACCP Process

https://youtu.be/dVbug89UHBA Welcome to a comprehensive Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points HACCP process exploration. In today’s world, ensuring the safety and quality of food products has become more crucial than ever. HACCP is a systematic approach that identifies and manages potential hazards throughout food production. By employing this science-based preventive system, businesses can minimize risks,
... Read moreNon Conformance Reports: A Step-by-Step Non-Conformance Investigation to Identifying and Resolving Issues

Non-Conformance Reports Introduction: In today’s fast-paced and competitive business landscape, identifying and resolving issues is crucial for maintaining the highest standards of quality and efficiency. Non-Conformance Product Reports (NCRs) are a powerful tool organizations can use to track and address deviations from standard procedures or specifications. By implementing a step-by-step approach to NCRs, companies
... Read moreFDA Cosmetics Regulations: A cosmetics business step-by-step guide
Introduction to Cosmetic Regulations by the FDA: Are you a cosmetics brand looking to navigate the complex world of FDA regulations? Look no further. Our step-by-step guide is here to demystify the process and help you stay compliant. In today’s highly regulated market, cosmetics brands must understand and adhere to FDA guidelines. Please do so
... Read moreNDI Classification Unlocked: The Ultimate Guide

When thinking about NDI Classification have you ever heard about the New Dietary Ingredient Notification in Ingredient Compliance? In today’s rapidly evolving world, businesses constantly seek innovative ways to gain a competitive edge. One such method is harnessing the power of NDI classification. NDI, or New Dietary Ingredient, refers to any ingredient not marketed in
... Read moreNavigating the Regulatory Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Health Canada Site Licenses

Are you a business owner in the health and wellness industry looking to navigate the complex regulatory landscape in Canada? Look no further! This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need about Health Canada Site Licenses. From understanding the requirements and application process to ensuring compliance with the regulations, our expert team has
... Read moreThe Role of FDA Agents in U.S. Compliance

In a world where the pharmaceutical industry is constantly evolving and new drugs are being introduced to the market every day, the role of US FDA agents has never been more important. These dedicated individuals are the unsung heroes who work tirelessly behind the scenes to safeguard public health and ensure the safety of the
... Read moreUltimate guide to Renewing FDA Registration: Stay Compliant and Keep Your Business Thriving

Are you a food, beverage, drug, or cosmetics business owner?If so, you already know how crucial it is to comply with Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulations. One of the key requirements for any business in the industry is to renew its FDA registration regularly. But why is this so important? In a constantly evolving
... Read moreThe Ultimate Guide to Conducting Successful Clinical Trials

Introduction: Welcome to the ultimate guide to conducting a successful clinical trial, where we will delve into the best practices and key considerations that can make or break the outcome of your research. Clinical trials are pivotal in advancing medical science and improving patient outcomes. However, executing a shot that yields reliable results requires meticulous
... Read moreFDA Toxicological Testing guidance for food additives Clinical Trials

The safety evaluation of direct food additives and color additives used in food will be evaluated in this blog post based on recommendations for the minimal toxicity tests to be undertaken. The details in this FDA guidance document can be used as broad guidelines for figuring out concern levels, the scope, and the types of toxicity testing
... Read moreThe Importance of Amazon Seller Compliance: How to Avoid Penalties and Boost Sales

In today’s competitive marketplace, selling products on Amazon has become a lucrative opportunity for many entrepreneurs and businesses. However, navigating the online retail world comes with challenges, particularly regarding Amazon seller compliance. Ensuring that your company follows all the rules and regulations set by Amazon is essential for maintaining a good reputation. Still, it can
... Read moreManaging FDA Fees: Budgeting and Planning for Success

Are you a company in the healthcare or pharmaceutical industry looking to bring a new product to market? If so, you’re probably aware of the complex and ever-changing regulatory landscape governed by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Navigating the FDA’s requirements is a challenging task, and one aspect that often catches businesses off guard
... Read moreA Guide to Health Canada Compliance for Health Businesses

In the ever-evolving healthcare landscape, staying up-to-date with the latest regulations and requirements is crucial for health professionals. And when it comes to navigating the complex world of Health Canada fees, knowledge is power. Understanding the ins and outs of these fees can help health professionals manage their budgets effectively and ensure compliance with regulatory
... Read moreFrom farm to fork: Why food regulations matter for food imported to Canada

https://youtu.be/mWaBQzsa1_M Introduction Welcome to a fascinating journey through the world of imported foods in Canada, where flavors from all corners of the globe converge on our plates. In an increasingly interconnected world, “farm to fork” has a new meaning. Gone are the days when our culinary choices were limited to local produce and traditional dishes.
... Read moreNavigating Health Canada’s NPN Number System: A Guide for Business Owners

Are you a business owner in the health and wellness industry? If so, you’re likely familiar with Health Canada’s Natural Products Number (NPN) system. Navigating this system can be a daunting task. Still, ensuring that your products comply with Canadian regulations is crucial. Our NHP License Experts can help you with this. With so much
... Read moreThe Ultimate PMA Submissions Guide: The Importance of Proper Documentation
Proper documentation is essential in any business operation and is particularly crucial when it comes to PMA submissions. Preparing and submitting a PMA (Pre-Market Approval) is complex and requires a meticulous approach. Every detail must be captured accurately and presented clearly and concisely. This is where the Ultimate PMA Submissions Guide comes in handy. It
... Read moreFDA guidance for EUA medical devices transition under PHE policies

The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) published two final guidelines on March 24, 2023, to help manufacturers of medical devices transition away from specific procedures and policies put in place during the COVID-19 Public Health Emergency (PHE). The guidelines give a general overview of the systems the FDA suggests businesses take to move their devices from PHE-era
... Read moreHow is the Drug Products Database revolutionizing healthcare?
The healthcare industry is constantly evolving, and with the introduction of new technologies, it is becoming more efficient and effective than ever before. One such game-changing innovation is the Drug Products Database, which revolutionizes how healthcare professionals and patients access medication information. This powerful tool is a comprehensive, user-friendly database that provides up-to-date information on
... Read moreHow to Stay Compliant With NHP Monograph Requirements
Consumers rely on Health Canada monographs to ensure the safety and efficacy of their products. But have you ever wondered how Health Canada decides which ingredients are safe to use in our medicines and supplements? This comprehensive guide outlines the standards for all licensed natural health products in Canada. Unlocking the secrets of these monographs
... Read moreGood Manufacturing Practices GMP for pharmaceutical companies
Introduction: When it comes to the pharmaceutical industry, there is no room for error. The production of pharmaceuticals requires strict adherence to quality standards to ensure the safety and efficacy of the final product. That’s where Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) come in. GMPs are guidelines and regulations that pharmaceutical manufacturers must follow to ensure their
... Read moreWhy compliance with the Canadian Consumer Product Safety Act is crucial for businesses

https://youtu.be/mWaBQzsa1_M If you’re a business owner looking to expand your reach into the Canadian market, importing products may be a viable option. However, navigating the regulations and requirements for importing goods into Canada can take time and effort. From customs clearance to taxes and duties, there are many factors to consider before bringing your products
... Read moreA Business Guide to Importing NMN Supplements Into Canada

As more and more people become health-conscious, the demand for supplements has skyrocketed. One of the most popular supplements on the market today is NMN (Nicotinamide mononucleotide), which is known for its anti-aging and health benefits. However, the process can seem daunting for businesses importing NMN supplements into Canada. With various regulations and restrictions, it
... Read moreHow to Meet Compliance Standards for Class II Medical Devices

Medical devices play a crucial role in modern healthcare, providing patients with life-changing treatments and improving the quality of life for millions worldwide. However, the development and manufacture of these devices are subject to strict regulatory requirements to ensure their safety and effectiveness. In particular, class 2 medical devices are subject to a range
... Read moreHow a Trusted Importer of Record Supports Medical Device Compliance
As a business owner in the medical industry, you understand the importance of providing quality products and services to your customers. When it comes to medical devices, ensuring they are safe and effective is paramount. Working with a reputable medical device importer is critical for your business. In today’s global economy, there are countless options
... Read moreThe Role of FSVP Certification in Global Food Safety

In today’s global food supply chain, ensuring the safety and quality of food products is critical to protecting public health and maintaining consumer confidence. With the increasing globalization of food production and distribution, there is a growing need for effective food safety management systems to identify and mitigate potential risks at every stage of the
... Read moreThe Role of Drug Identification Numbers in Prescription Compliance
The healthcare industry is constantly evolving, and one of the most significant advances has been implementing drug identification numbers (DINs). These unique numbers assigned to each medication are crucial in streamlining the prescription process and ensuring patient safety. With the rise of online pharmacies and the increasing complexity of drug interactions, DINs have become a
... Read moreStreamlining Imports With an Importer of Record

Importing goods from other countries can be a lucrative business and a complex and tedious process. As an importer, you must navigate a maze of regulations, tariffs, and customs procedures that vary from country to country. That’s where an Importer of Record (IOR) comes in. An IOR is a professional service provider that can help
... Read moreA complete guide to 510k submissions: Everything you should know
As a medical device manufacturer, getting your product to market can be a complex process with various regulatory requirements to fulfill. One of the most essential steps in getting your device approved for sale in the United States is submitting a 510(k) application to the FDA. However, navigating the 510(k)-submission process can take time and
... Read moreHealth Canada interim policy extension on importing and selling infant formula

Introduction: By extending the interim policy on the importation and sale of infant formulas, human milk fortifiers, and dietary products to treat inborn errors of metabolism, Health Canada intends to continue addressing shortages of infant formula and other foods for a particular nutritional purpose. This Health Canada notice also outlines the department’s plans for public consultation in
... Read moreEverything You Need to Know About Importing Products Into Canada

If you’re a business owner looking to expand your reach into the Canadian market, importing products may be a viable option. However, navigating the regulations and requirements for importing goods into Canada can take time and effort. From customs clearance to taxes and duties, there are many factors to consider before bringing your products across
... Read moreKey Strategies to Improve Drug Submission Success
In the pharmaceutical industry, proper drug submission management is crucial to the success of any drug development process. The submission process can be daunting, complex, and time-consuming. Still, it plays a vital role in ensuring that a drug gets approved by regulatory authorities and reaches critical patients. The consequences of poor submission management can be
... Read moreEmergency Alert: NNHPD proposed fees may lead to business closures
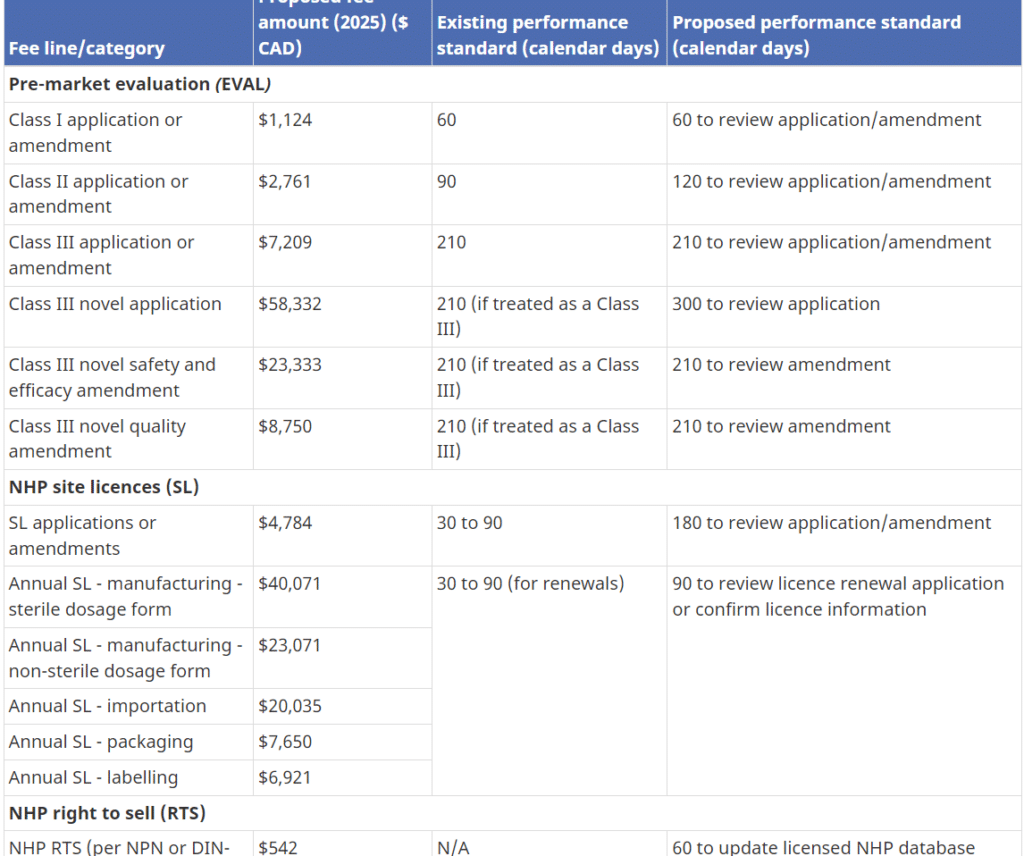
Health Canada has the authority to set and charge health product fees under the Food and Drugs Act (FDA). On May 12th, 2023, Health Canada published a proposal with a massive mandatory cost impact for the industry and consumers in the following areas: NHPs Annual Right to Sell (RTS) NHP Product License Applications (PLA) NHP
... Read moreFrom HACCP to CCPs: How Food Safety Standards Have Changed

The food industry has undergone a significant transformation in terms of safety and quality control over the years. From the early days of Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) to the current Critical Control Points (CCPs) system, food safety standards have become more stringent and comprehensive. As a professional in the food industry, it’s
... Read moreNNHPD Improvements to support NHP site licensing
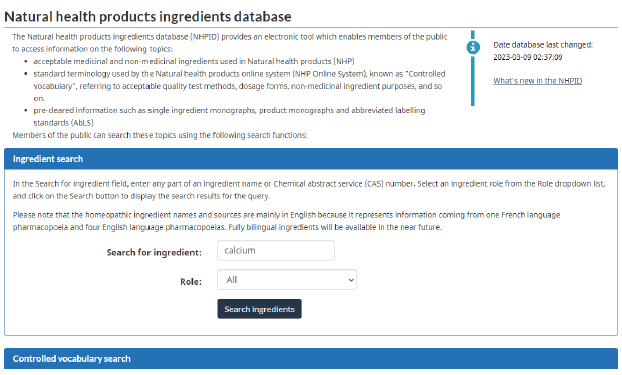
What improvements are being made to support NHP site licensing? Internal template updates support: consistency between reviews-Fall 2023 Increased efficiencies in Site Licensing-Summer/Fall 2022Continue risk-based administrative renewals. Looking to provide advance notice to lighten the burden of application and working with ROEB on leveraging inspection ratings Targeted updates to FPS User Guide*-December 15, 2022 -Test
... Read moreThe Importance of Food Safety Plans for Food Businesses

Are you considering getting your food safety certification? In today’s highly competitive food industry, ensuring your food products are safe for consumption is paramount. With the increasing number of foodborne illnesses and outbreaks, consumers are becoming more aware of the need for food safety certifications. As a food business owner, prioritizing food safety certifications not
... Read moreThe cost of HACCP Certification: Everything to know about the Investment

https://youtu.be/dVbug89UHBA HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) certification is a food safety management system that helps businesses identify and control potential hazards in their food production process. While the cost of implementing a HACCP program may seem daunting, the benefits of certification can far outweigh the initial investment. In this guide, we’ll explore the
... Read moreWhy an FSVP Importer Is Essential for Food Safety

As our world becomes increasingly globalized, the importation of food has become a common practice. However, with growing concerns about food safety and compliance, we must ensure our food is safe and meets all regulatory requirements. This is where the FSVP importer comes in. FSVP, or the Foreign Supplier Verification Program, is a critical
... Read moreHow GRAS Notification Supports FDA Food Ingredient Approval

Introduction: In the dynamic realm of food innovation, ushering in new ingredients responsibly and securely is of paramount importance. This article is your guide through the systematic GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe) notification process—a vital pathway that paves the way for the approval and integration of novel ingredients. Join us as we demystify the step-by-step
... Read moreUnderstanding FDA Furls and Their Impact on Medical Device Companies

https://youtu.be/yvnTszySkgg If you’re in the medical device manufacturing business, you’re likely familiar with the FDA’s regulations, including FDA Furls. However, understanding these regulations can be complex and confusing. This guide breaks down FDA Furls into easy-to-understand terms, so you can better understand how they affect your business. What are FDA Furls, and why do they
... Read moreFTC puts nearly 700 companies on notice of product claim civil penalties

Introduction: On April 13th, the Federal Trade Commission sent letters to warn hundreds of marketers to refrain from misleading customers with product claims in their marketing material that cannot be supported or substantiated. The FTC issued notifications to the businesses warning that it would not hold back in using its power to pursue offenders with severe civil
... Read moreNavigating the GRAS process: A guide for food manufacturers

https://youtu.be/iVJlCZmDeWU Introduction: If you’re a food manufacturer, you need to understand the generally recognized as safe (GRAS) process. This process determines whether a substance is safe to use in food products without the need for pre-market approval from the FDA. This guide will provide you with a comprehensive overview of the GRAS process, including its
... Read moreHow to get your Food Handlers License: Ultimate 5 step guide

https://youtu.be/NN8ZLynq6kE If you work in the food service industry, you may need to obtain food handlers license to ensure that you are properly trained in food safety and handling. This guide will walk you through the steps to get certified, including training requirements, exam preparation, and application procedures. We’ll also provide timing estimates and let
... Read moreEverything you should know about FDA GRAS Status in 2023

https://youtu.be/wOKeuDAEfss Have you ever wondered what it means for a food or ingredient to be ‘Generally Regarded as Safe’ (GRAS)? This article will explain what GRAS is and how to obtain it from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) so you can stay updated on the latest FDA regulations. What is GRAS Status? GRAS
... Read moreThe role of Critical Control Points in your HACCP Plan

https://youtu.be/dVbug89UHBA In the food industry, ensuring the safety of the products you produce is of utmost importance. One key aspect of this is understanding critical control points (CCPs) and implementing measures to control them. Critical control points (CCPs) are specific points in the food production process where potential hazards can be controlled or eliminated to
... Read moreSoftware as Medical Devices (SaMD) Registration: What You Should Know
As technology continues to advance, the use of Software as Medical Devices (SaMD) is becoming more prevalent in the healthcare industry. SaMD refers to software that is intended for medical purposes, such as diagnosing or treating a disease. However, with the rise of SaMD comes the need for regulations to ensure their safety and effectiveness.
... Read moreBRC Certification Explained for Canadian Businesses

BRC certification is a globally recognized standard for food safety and quality management. In Canada, it has become increasingly important as retailers and consumers expect safer and more reliable food products.This guide offers an easy-to-read overview of BRC certification requirements, the process, benefits, and common challenges for Canadian food businesses. What is BRC certification? BRC
... Read moreTop 5 benefits of hiring an Importer of Record for International Trade

https://youtu.be/mWaBQzsa1_M Introduction Importing goods can be a complex process, especially when it comes to navigating customs regulations and compliance requirements. That’s where an importer of record (IOR) can come in handy. By working with an experienced IOR, you can save time, money, and avoid potential headaches that come with importing goods. Learn more about the
... Read moreGRAS List for Food Additives – Your Step-by-Step Guide to Safety

https://youtu.be/wOKeuDAEfss Have you ever wondered what goes into the food you eat every day? Various food additives enhance our food’s taste, texture, and appearance, from the preservatives in your favorite snacks to the color additives in your morning cereal. But how do we know that these additives are safe for consumption? That’s where the FDA
... Read moreFDA to close VCRP to prepare for MOCRA registration in 2023

Introduction: In a recent update released on March 27, 2023, the FDA announced it has stopped accepting and processing VCRP submissions to the Voluntary Cosmetics Registration Program. Instead, in accordance with the Modernization of Cosmetics Regulation Act of 2022, the FDA is creating a programme that cosmetic businesses will use to submit facility registrations and cosmetic product
... Read moreA Guide to Dietary Supplement Regulations

Navigating the complexities of the regulatory requirements for dietary supplements can be daunting. However, by understanding the framework, you can help to ensure your supplements are safe and effective, while keeping your business up-to-date on changes to the regulatory landscape. This guide provides you with the information you need to stay informed about the FDA
... Read moreHow to get GRAS Certified faster in 2023?

https://youtu.be/iVJlCZmDeWU GRAS certification is an important step for any manufacturer who wants to market a food or food-related product. By following the proper procedures, you can ensure that your product is recognized as safe and accelerate the approval process so it can reach the market faster. This guide will provide you with an overview of
... Read moreWhat you should know about FDA Approvals for Drugs & Medical Devices
Introduction: FDA approvals can be a complex process, but understanding its important steps can give you insight into how drugs and medical devices enter the marketplace. From registering with the FDA to undergoing drug/device tests and inspections, find out all about FDA approvals here. What is the FDA and it’s role in regulating drugs &
... Read moreHow to comply with Health Canada Regulations for Medical Devices?
Introduction: Manufacturing and selling medical devices in Canada can be a complex process and requires adherence to Health Canada’s strict regulations. Understanding these regulations is essential for product safety, quality assurance, and compliance with the Canadian Medical Devices Regulations (CMDR). Understand Health Canada’s Safety Standards and Regulations: It’s important to ensure that a medical
... Read moreFDA Registration Renewals: FDA Increases Facility Enforcement

As a business owner, keeping up with regulatory requirements is a top priority. One such requirement is the FDA’s renewal registration. The process of registering your facility with the FDA can be confusing, but it’s essential to comply in order to avoid penalties or even shutting down your operation. Introduction: The American Food and Drug
... Read moreUnderstanding the Costs of MDL and MDEL Approvals

The price for an MDEL (Medical Device Establishment Licence) and MDL (Medical Device Licence) in Canada varies according to the categorization of the medical device. We will compare the prices for both MDELs and MDLs in this blog post according to their class. MDEL (Medical Device Establishment Licence) The total price of MDEL varies between
... Read moreFDA Fees for Medical Device Establishment Registration in 2023
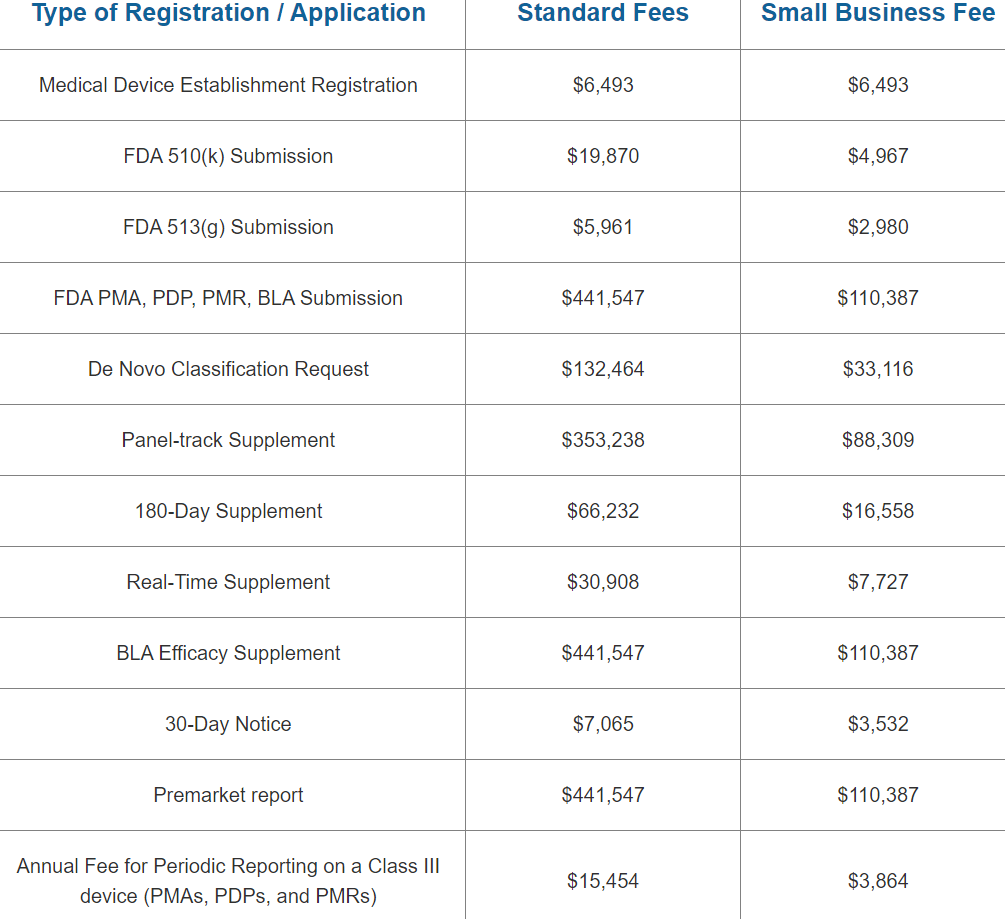
The cost to register an FDA Medical Device Establishment is USD $6,493 for 2023. The FDA’s fiscal year 2023 begins on October 1 and runs through September 30. Between October 1, 2022, and December 31, 2022, the yearly establishment registration fee must be paid. A reduced small company charge is NOT applicable to the
... Read moreWhat Companies Need to Understand About GRAS Ingredients

Introduction to GRAS: Understanding the regulations and safety risks associated with GRAS ingredients can be tricky, but it doesn’t have to be. This comprehensive guide gives you a detailed overview of GRAS ingredients and the regulations governing their use in food products, so you can get up to speed quickly. Your food scientists and our
... Read moreThe Importance of HACCP Consultants for Food Safety

Introduction: Food safety is an important part of any food business. It’s also a complicated one. There are many regulations and laws to take into consideration, and they can often be confusing to someone who isn’t trained in food safety or quality management. That’s where HACCP comes in: the Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points
... Read moreEverything You Should Know About the NHP Database (LNHPD)

If you plan to manufacture, import, or sell a natural health product (NHP) in Canada, you need to understand the Licensed Natural Health Products Database (LNHPD). This official database lists every NHP that has been approved for sale with a Natural Product Number (NPN). Getting your product licensed and listed in the LNHPD is a
... Read moreHow to Choose the Right Importer: 5 Essential Tips

Looking for a quality import service can be a daunting task, but with the right advice and tips, you can find the perfect fit for your business. This decision becomes even more critical when importing CPG goods. Here are 5 essential factors to consider when choosing an import service provider. 1. Research Companies Thoroughly When
... Read moreUnderstanding Class I Medical Devices Approval With Health Canada

What are Class 1 Medical Devices? Class 1 medical devices are the lowest risk category of medical devices, as they are considered to have a low potential for harm to the user. These devices are typically simple in design and do not require a lot of regulatory oversight. Examples of class 1 medical devices include
... Read moreMDEL, DEL, DIN & PRMA Application Fee Amendments for 2023

PMRA Annual Fees reduced for Reporting and Applications: Health Canada is implementing a new approach beginning April 1, 2023. The PMRA will no longer contact registrants who fail to submit their volumetric sales report by the June 1st deadline. Registrants who do not submit their volumetric sales report by the June 1st deadline will face
... Read moreUnderstanding HACCP: 7 Principles Every Food Business Should Know
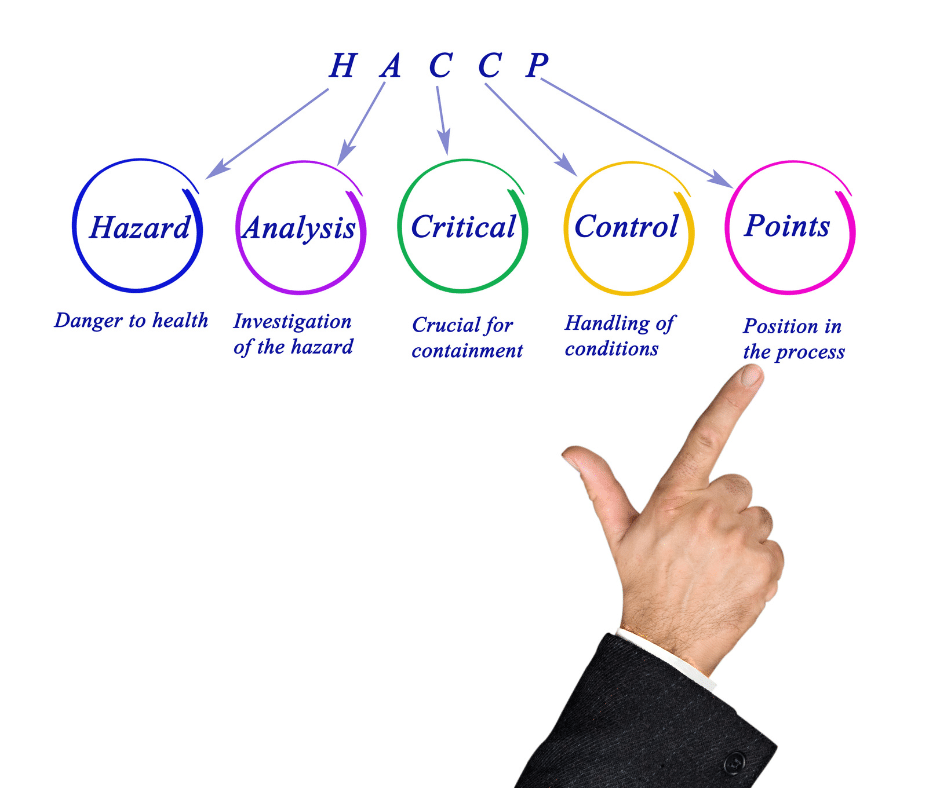
The purpose of a Hazard Analysis Critical Control Points (HACCP) plan is to identify and control any hazards that may arise during the process of manufacturing, storing, distributing, and consuming food products. Ensuring food safety is a critical component of the food industry. HACCP, or Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points, is the system used
... Read moreMDR Amendments COVID-19 Medical Devices Importing & Sales
Background: Health Canada issued three interim orders to allow the importation and sale of medical devices used to diagnose, treat, mitigate, or prevent COVID-19. Interim orders were issued to speed up access to these medical devices in Canada during the pandemic. Interim Order No. 3 Concerning the Importation and Sale of Medical Devices for Use
... Read moreHealth Canada Labelling & Cosmetic Notification changes in 2023

Introduction: The sections relating to the disclosure of fragrance allergens because of the regulations go into effect two years following the date the Regulations concerning cosmetic ingredients. Six months following the date of registration, all other rules would take effect. In this article, we discuss the issues that lead to Health Canada’s cosmetic notification proposal
... Read moreGMP Certification Made Simple: What Companies Should Know

Are you considering obtaining GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) certification for your business? The GMP certification process is crucial for ensuring your products meet rigorous safety, quality, and regulatory standards. Whether you are in the pharmaceutical, food, or dietary supplement industries, this certification not only helps maintain the highest quality but also supports compliance with global
... Read moreCosmetic Labelling Rules Every Business Should Understand

Introduction: Cosmetic labelling is an essential part of developing and marketing cosmetics. Companies must meet government requirements for labelling, including ingredient listings, cautions and warnings, cosmetic claims, directions for use and other information needed for safety and consumer understanding. This guide outlines the necessary requirements of cosmetic labelling in Canada. Understanding Cosmetic Labelling Regulations and
... Read moreFDA Draft Guidance Labeling Plant Based Milk Alternatives in 2023

Introduction: The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued draft guidance for comment today to help ensure appropriate labelling of plant-based products marketed and sold as alternatives to milk (plant-based milk alternatives, or PBMA). This draft guidance will provide industry with recommendations that will result in clear labelling, allowing consumers to make more informed purchasing
... Read moreHealth Canada Latest Draft Guidance (Biologic Regulations, Drug Labelling, NDS/ANDS & Drug Submissions Rolling Reviews)
Introduction: Submitting a new drug to Health Canada can be a complex and time-consuming process. This post will provide essential information about the regulations, legal requirements, and specific steps involved in the submission process for new drugs in Canada. Health Canada has been busy lately releasing several draft guidance documents related to drug compliance
... Read moreFiling a Medical Device 510(k): Timing and Process Explained
Introduction: A 510(k) clearance is a process by which medical device manufacturers notify the FDA of their intent to market a new device that is substantially equivalent to a legally market device. Submitting a 510k to the FDA is an important step for any business or healthcare product that needs to be approved for sale.
... Read moreHow to Navigate Regulatory Requirements for Class III Medical Devices
Introduction: Class 3 medical devices are subject to the highest level of scrutiny and require special attention when it comes to meeting their regulatory requirements. This article will discuss what it takes for Class 3 medical devices to meet these stringent requirements. Class 3 medical devices are especially complex and pose the highest risk to
... Read moreWhat Does It Mean to be GFSI Certified in an FSMA Environment?

Introduction: FSMA stands for the “Food Safety Modernization Act” which is a set of laws enacted by the US government to ensure food safety and decrease the risk of foodborne illness. Congress enacted FSMA in response to dramatic changes in the global food system and in our understanding of foodborne illness and its consequences, including
... Read moreGFSI Certification Requirements: How to get GFSI Certified?

https://youtu.be/XRZ87ifRki0 Introduction: The Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI) is an international organization that sets standards for food safety and quality assurance. It was founded by the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), World Health Organization (WHO), and World Trade Organization (WTO). The Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI) is a collaboration between the world’s leading
... Read moreFDA to tighten regulatory process around CBD food & supplements

Introduction: The FDA may have turned a blind eye to companies like Bio Steel in the past who’ve been selling supplements containing CBD in the United States but they’re like to start issuing more warning letters when drug claims are made. With the FDA enforcement of CBD supplements being like pet supplements the FDA is
... Read more10 tips to Prepare for the Safe Food License Application Process

Introduction: There are many reasons that you might want to get licensed as a food processor or retail operator. You might be interested in expanding your business, or you might want to make sure that your food safety program is compliant with new regulations. Regardless of the reason, it’s important to know what you’re getting
... Read moreClearing Regulatory Hurdles with a 510K Premarket Notification
Submitting a 510K Premarket Notification is an essential step in the process of getting medical devices approved by the FDA. This notification includes detailed information about the device and its intended use and data regarding safety and efficacy. Learn more about the procedure for submitting a 510K Premarket Notification here. What is the 510k
... Read moreMaking the Most of the FDA GRAS Database for Ingredient Safety

If you’re in the food or ingredient industry, you’ve likely heard about the FDA GRAS database. It’s a vital resource for businesses seeking clarity on whether a substance is Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) for use in food products. Knowing how to navigate the FDA GRAS database not only helps you stay compliant, it also
... Read more