 Introducing the Supplemented Foods Facts Table (SFFT), your go-to guide for navigating the ever-changing world of supplemented foods. With consumer demand skyrocketing for these products, grasping the SFFT is vital for businesses looking to excel in this booming market.
Introducing the Supplemented Foods Facts Table (SFFT), your go-to guide for navigating the ever-changing world of supplemented foods. With consumer demand skyrocketing for these products, grasping the SFFT is vital for businesses looking to excel in this booming market.
In this article, we’ll unravel everything you need to know about the SFFT, from its purpose to its must-follow rules. We’ll also explore how it can empower your business to effectively convey your supplemented food products’ benefits and nutritional value to consumers. Whether you’re a fresh-faced startup or a seasoned brand, consider this article your trusty companion for mastering the Supplemented Foods Facts Table.
Whether you’re a small startup or an established brand, this article is your go-to resource for understanding and complying with the SFFT. Stay ahead of the competition and enhance consumer trust by mastering the ins and outs of the Supplemented Foods Facts Table.
Why is the SFFT important for businesses?
The Supplemented Foods Facts Table (SFFT) is an essential tool for businesses operating in the supplemented foods industry. This table gives businesses a standardized format to communicate important product information to consumers. By including the SFFT on product labels, companies can ensure that consumers can access accurate and transparent information about their supplemented food products’ nutritional content and benefits.
The SFFT is crucial in building consumer trust and confidence in supplemented foods. With the increasing interest in health and wellness, consumers are becoming more conscious about the nutritional value of their products. By providing clear and comprehensive information through the SFFT, businesses can meet this demand and differentiate themselves in the market.
Furthermore, the SFFT helps businesses comply with regulatory requirements. Many countries have specific regulations that mandate the use of SFFT on product labels. By adhering to these regulations, companies can avoid potential legal issues and ensure that their products comply with industry standards.
In summary, the SFFT is essential for businesses because it allows them to communicate vital information to consumers, build trust, comply with regulations, and differentiate themselves in the competitive supplemented foods market.
What are the components of the Supplemented Foods Facts Table SFFT?
To effectively create a compliant SFFT for your products, it is essential to understand the critical components of the table. The SFFT consists of several sections, each providing specific information about the supplemented food product. Let’s take a closer look at these components:
1. Serving Size: This section indicates the recommended serving size of the product. Determining an appropriate serving size that accurately reflects how consumers typically consume the product is vital.
2. Calories: The product’s calorie content is displayed in this section. It provides consumers with an understanding of the energy value of the product.
3. Total Fat: This section includes information about the total fat content of the product, including the amount of saturated and trans fats. It is essential to disclose this information as it helps consumers make informed choices about their dietary intake.
4. Cholesterol: The cholesterol content of the product is displayed in this section. High cholesterol levels can have adverse health effects, so providing this information to consumers is essential.
5. Sodium: This section indicates the sodium content of the product. High sodium intake can harm health, so disclosing this information allows consumers to manage their sodium intake effectively.
6. Total Carbohydrates: This section provides information about the total carbohydrate content of the product, including dietary fiber and sugars. It helps consumers understand the carbohydrate composition of the product, which is particularly important for individuals following specific diets.
7. Protein: The product’s protein content is displayed in this section. Protein is an essential nutrient, and disclosing this information helps consumers decide based on their dietary needs.
8. Vitamins and Minerals: This section lists the vitamins and minerals present in the product and their respective quantities. It is crucial to provide this information as it allows consumers to assess the product’s nutritional value.
By understanding these components, businesses can create a comprehensive and accurate SFFT for their supplemented food products.
How do you create a compliant SFFT for your products?
Creating a compliant SFFT for your products involves following specific guidelines and regulations. Here are the steps to ensure your SFFT meets the requirements:
1. Research Regulatory Requirements: Research the specific regulatory requirements for SFFT in your target market. Different countries may have varying guidelines and regulations, so it is crucial to understand and comply with the relevant standards.
2. Gather Accurate Nutritional Data: Collect accurate and up-to-date nutritional data for your supplemented food products. This includes information on serving sizes, calories, fats, cholesterol, sodium, carbohydrates, protein, vitamins, and minerals. Ensure that a reputable source or laboratory verifies the data.
3. Organize the SFFT: Use a standardized format to organize the SFFT. The table should be clear, readable, and prominently displayed on the product label. Use bold headings, appropriate font size, and spacing to enhance readability.
4. Calculate Percent Daily Values: The percent daily values (%DV) for each nutrient listed in the SFFT. %DV indicates the proportion of a specific nutrient in the product relative to the recommended daily intake. This information helps consumers understand the nutritional significance of the product.
5. Review for Accuracy and Compliance: Double-check the SFFT for accuracy and compliance with regulatory requirements. Ensure that all information is correctly displayed and that there are no misleading or false claims. It is advisable to consult with experts or regulatory bodies to verify the compliance of your SFFT.
By following these steps, businesses can create a compliant SFFT that provides accurate and transparent information to consumers.
Tips for optimizing your SFFT for consumer understanding
Creating a compliant SFFT is essential, but optimizing the table for consumer understanding is equally important. Here are some tips to help you achieve this:
1. Use Simple Language: Avoid technical jargon and use simple language that is easy for consumers to understand. Break down complex terms and provide explanations where necessary.
2. Provide Context: Supplement the SFFT with additional information or context to help consumers make informed decisions. For example, you can briefly describe the product’s benefits or usage instructions.
3. Consider Visual Aids: Incorporate visual aids, such as icons or symbols, to enhance the readability of the SFFT. These visual cues can help consumers quickly identify essential information, such as allergen warnings or nutritional highlights.
4. Highlight Key Nutrients: Use formatting techniques, such as bold or colored text, to highlight critical nutrients or beneficial ingredients. This can draw consumers’ attention to the nutritional value of the product.
5. Include Additional Information: Consider including additional information, such as allergen statements, dietary claims, or certifications, to further enhance consumer understanding and trust.
By optimizing the SFFT for consumer understanding, businesses can effectively communicate their supplemented food products’ benefits and nutritional value.
What are the common mistakes to avoid when creating an SFFT?
While creating an SFFT, businesses should be aware of common mistakes that can compromise the accuracy and compliance of the table. Here are some errors to avoid:
1. Inaccurate Nutritional Data: Ensure that the nutritional data used in the SFFT is accurate and current. Refrain from relying on outdated or incorrect information to mislead consumers and result in non-compliance with regulations.
2. Misleading Serving Sizes: Provide serving sizes that accurately reflect how consumers consume the product. Misleading serving sizes can misrepresent the product’s nutritional content and confuse consumers.
3. Omitting Key Nutrients: Include all relevant nutrients in the SFFT. Omitting vital nutrients can mislead consumers and result in non-compliance with regulations.
4. False or Misleading Claims: Avoid making false or misleading claims in the SFFT. All information should be accurate, transparent, and supported by scientific evidence.
5. Non-compliance with Regulations: Stay updated with the latest regulations and guidelines for SFFT. Non-compliance can lead to legal issues and damage the reputation of your business.
By avoiding these common mistakes, businesses can ensure the accuracy, compliance, and effectiveness of their SFFT.
What is the role of the SFFT in product labeling and marketing?
The Supplemented Foods Facts Table (SFFT) is vital in product labeling and marketing. Here’s how the SFFT contributes to these aspects:
1. Transparency and Consumer Trust: By including the SFFT on product labels, businesses demonstrate transparency and provide consumers with accurate and comprehensive information about their supplemented food products’ nutritional content and benefits. This builds trust and confidence in the brand.
2. Differentiation and Competitive Advantage: The SFFT allows businesses to differentiate by highlighting their products’ nutritional value and benefits. Companies can attract health-conscious consumers and gain a competitive advantage by effectively communicating this information.
3. Educating Consumers: The SFFT is an educational tool that helps consumers make informed choices about their dietary intake. By providing clear and understandable information, businesses empower consumers to make healthier and more conscious decisions.
4. Compliance with Regulations: The SFFT ensures compliance with regulations set by governing bodies. By adhering to these regulations, businesses avoid legal issues and maintain the integrity of their product labeling.
The SFFT is crucial in product labeling and marketing by promoting transparency, differentiation, consumer education, and regulation compliance.
What are the regulatory considerations for the SFFT?
When creating an SFFT, businesses must consider the specific regulatory requirements in their target market. Here are some regulatory considerations to keep in mind:
1. Country-specific Guidelines: Different countries may have specific guidelines and regulations for SFFT. Research and understand the requirements of your target market to ensure compliance.
2. Language Requirements: Some countries may have language requirements for the SFFT. Ensure that the table is presented in the appropriate language(s) for your target market.
3. Formatting and Placement: Regulatory bodies may have specific requirements for the formatting and placement of the SFFT on product labels. Familiarize yourself with these guidelines to ensure compliance.
4. Health Claims and Disclaimers: Some countries have strict regulations regarding health claims and disclaimers on product labels. Ensure that any claims made in the SFFT are supported by scientific evidence and comply with these regulations.
5. Updates and Changes: Stay updated with any changes or updates to the regulatory requirements for SFFT in your target market. Regularly review and revise your SFFT to ensure continued compliance.
By considering these regulatory aspects, businesses can create an SFFT that meets the specific requirements of their target market.
Resources for businesses to learn more about the SFFT
As businesses navigate the world of supplemented foods and the requirements of the Supplemented Foods Facts Table (SFFT), it is essential to have access to reliable resources. Here are some valuable resources to learn more about the SFFT:
1. Regulatory Bodies: Consult the websites and publications of regulatory bodies in your target market. These organizations often provide detailed guidelines and resources related to SFFT.
2. Industry Associations: Join industry associations or organizations specializing in the supplemented foods sector. These associations often provide resources, webinars, and workshops to help businesses understand and comply with SFFT requirements.
3. Professional Consultants like Quality Smart Solutions: Seek guidance from professional consultants who specialize in food labeling and compliance. These experts can provide personalized advice and assistance tailored to your business needs.
4. Online Research: Conduct online research to access articles, studies, and publications related to the SFFT. Many reputable sources provide free information and resources to help businesses better understand the topic.
Remember to verify the credibility and relevance of the resources you consult to ensure accurate and up-to-date information.
Conclusion: The future of the SFFT in the food industry.
The Supplemented Foods Facts Table (SFFT) is an essential tool for businesses operating in the supplemented foods industry. As consumer demand for transparent and nutritious products continues to rise, the SFFT plays a crucial role in providing accurate and comprehensive information to consumers. By understanding the components of the SFFT, following regulatory guidelines, and optimizing the table for consumer understanding, businesses can effectively communicate the benefits and nutritional value of their supplemented food products. Compliance with regulations ensures transparency, builds consumer trust, and enhances the competitiveness of businesses in the market.
As the food industry evolves, the SFFT will likely play a significant role in product labeling and marketing. By staying updated with regulatory changes and industry trends, businesses can adapt and thrive in the dynamic landscape of supplemented foods. Remember, the Supplemented Foods Facts Table is not just a regulatory requirement but an opportunity for businesses to showcase their commitment to transparency, health, and consumer satisfaction. Mastering the ins and outs of the SFFT will position your business for success in the ever-growing market of supplemented foods.

Click here to learn about the Supplemented Facts Table Regulations.
Quality Smart Solutions has a team of professionals to offer support from day one of starting your business, including formulation and label reviews, Veterinary Health Product notifications and more.

























 Selling cosmetics on Amazon Canada can open up a world of opportunity, but it comes with strict compliance expectations. Recently, many sellers have faced Amazon Canada cosmetic delisting due to missing or incomplete regulatory documentation. This issue not only disrupts sales but can damage your brand’s reputation and standing with Amazon.
Selling cosmetics on Amazon Canada can open up a world of opportunity, but it comes with strict compliance expectations. Recently, many sellers have faced Amazon Canada cosmetic delisting due to missing or incomplete regulatory documentation. This issue not only disrupts sales but can damage your brand’s reputation and standing with Amazon.







 If you’re trying to bring a food or supplement product to both the Canadian and US markets, you’ve probably already noticed how complicated labeling can get. Maybe you’ve had a label approved in one country but rejected in the other, or you’ve found yourself buried in pages of inconsistent regulations. You’re not the only one facing this.
If you’re trying to bring a food or supplement product to both the Canadian and US markets, you’ve probably already noticed how complicated labeling can get. Maybe you’ve had a label approved in one country but rejected in the other, or you’ve found yourself buried in pages of inconsistent regulations. You’re not the only one facing this.
 On March 13, 2025, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) released its first public summary data on the mandatory registration of cosmetic product facilities and the listing of cosmetic products, as required under the Modernization of Cosmetics Regulation Act of 2022 (MoCRA).
On March 13, 2025, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) released its first public summary data on the mandatory registration of cosmetic product facilities and the listing of cosmetic products, as required under the Modernization of Cosmetics Regulation Act of 2022 (MoCRA).






 The self-affirmed GRAS pathway may soon be eliminated. On March 10, 2025, HHS Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr. directed the FDA to explore rulemaking to remove the option for companies to self-affirm that food ingredients are safe. If implemented, this shift will require all GRAS determinations to undergo FDA review, significantly altering the regulatory landscape for food manufacturers.
The self-affirmed GRAS pathway may soon be eliminated. On March 10, 2025, HHS Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr. directed the FDA to explore rulemaking to remove the option for companies to self-affirm that food ingredients are safe. If implemented, this shift will require all GRAS determinations to undergo FDA review, significantly altering the regulatory landscape for food manufacturers.




 Health Canada’s 2026 Fragrance Allergen Rules: What You Need to Know
Health Canada’s 2026 Fragrance Allergen Rules: What You Need to Know
 Introduction
Introduction

 Understanding ‘Made in Canada’ Claims
Understanding ‘Made in Canada’ Claims
 Bringing a new substance into Australia’s listed medicines market can be challenging. The
Bringing a new substance into Australia’s listed medicines market can be challenging. The 
 Navigating the FDA compliance process for shilajit can be challenging, especially if you’re new to the regulatory landscape. As shilajit gains popularity in the U.S. for its health benefits, it’s crucial to ensure your product meets FDA requirements before introducing it to the market. Understanding these steps from the beginning can help you streamline the process and avoid delays.
Navigating the FDA compliance process for shilajit can be challenging, especially if you’re new to the regulatory landscape. As shilajit gains popularity in the U.S. for its health benefits, it’s crucial to ensure your product meets FDA requirements before introducing it to the market. Understanding these steps from the beginning can help you streamline the process and avoid delays.



 Understanding the FDA classification system for medical devices is key to getting your product to market safely and efficiently. Knowing how the
Understanding the FDA classification system for medical devices is key to getting your product to market safely and efficiently. Knowing how the 
 Are you ready for the upcoming changes to Health Canada Fees in 2025? These fees, effective from April 2025, impact businesses dealing with drugs, medical devices, and cannabis. With updates spanning licensing, submissions, and compliance requirements, staying informed is key to avoiding disruptions.
Are you ready for the upcoming changes to Health Canada Fees in 2025? These fees, effective from April 2025, impact businesses dealing with drugs, medical devices, and cannabis. With updates spanning licensing, submissions, and compliance requirements, staying informed is key to avoiding disruptions.


 Are you trying to make sense of the FDA’s 510(k) pre-submission process? You’re not alone. Many companies, especially those new to the regulatory landscape, find themselves wondering where to start, what’s required, and how to get FDA approval for their medical devices. Without a clear plan, it’s easy to waste time and money on unnecessary steps, or worse, miss critical requirements that delay approval by years.
Are you trying to make sense of the FDA’s 510(k) pre-submission process? You’re not alone. Many companies, especially those new to the regulatory landscape, find themselves wondering where to start, what’s required, and how to get FDA approval for their medical devices. Without a clear plan, it’s easy to waste time and money on unnecessary steps, or worse, miss critical requirements that delay approval by years.




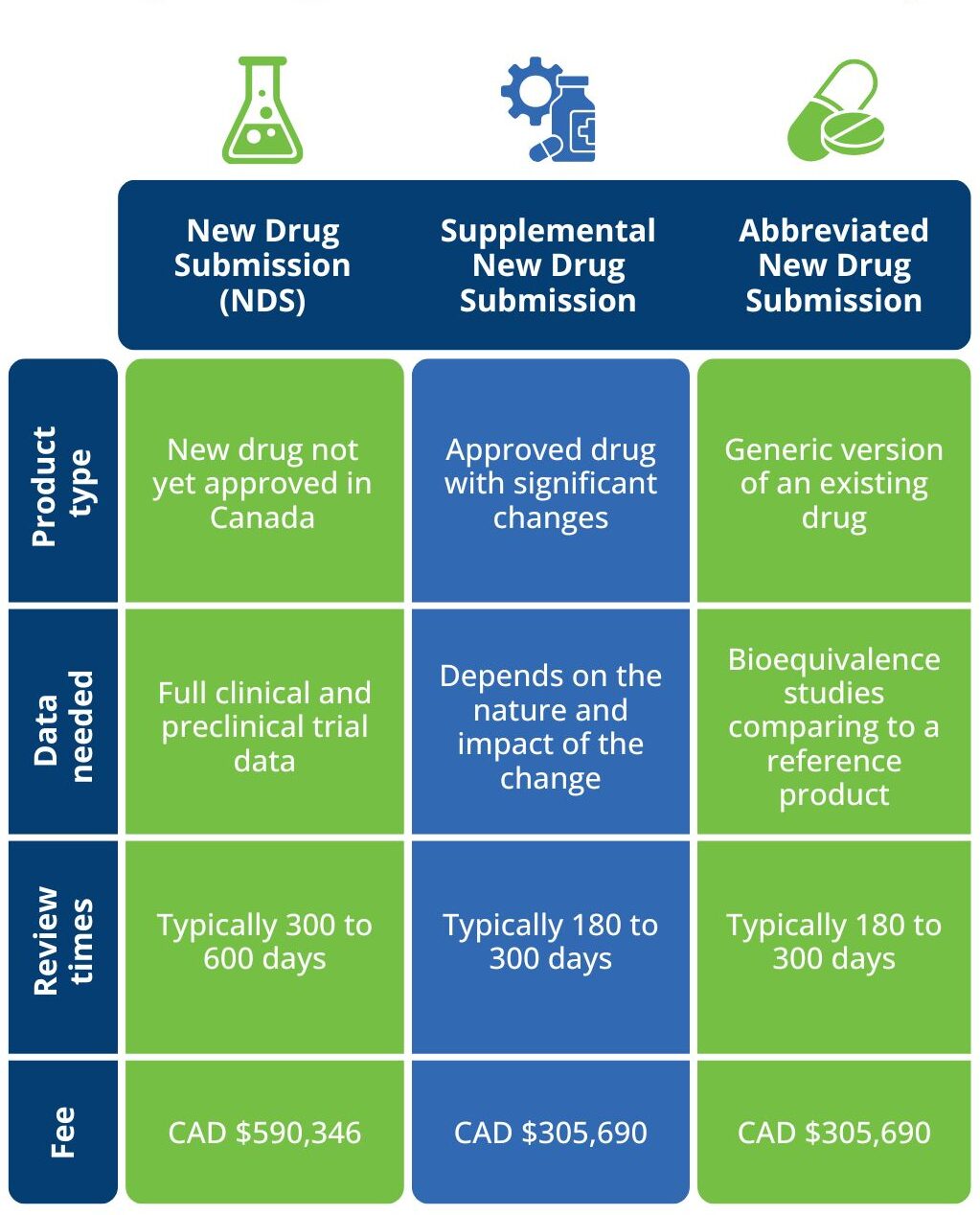 Frequently asked questions
Frequently asked questions
 If you’re bringing a drug or health product to the Canadian market, you’ll need to understand Health Canada’s regulations. Two important terms you’ll come across are Drug Monographs and Product Monographs. While they sound similar, they serve different purposes. Knowing the difference can help you navigate approvals smoothly and avoid delays.
If you’re bringing a drug or health product to the Canadian market, you’ll need to understand Health Canada’s regulations. Two important terms you’ll come across are Drug Monographs and Product Monographs. While they sound similar, they serve different purposes. Knowing the difference can help you navigate approvals smoothly and avoid delays.





 The Stakes Are High—Don’t Let Your Brand Get Left Behind
The Stakes Are High—Don’t Let Your Brand Get Left Behind








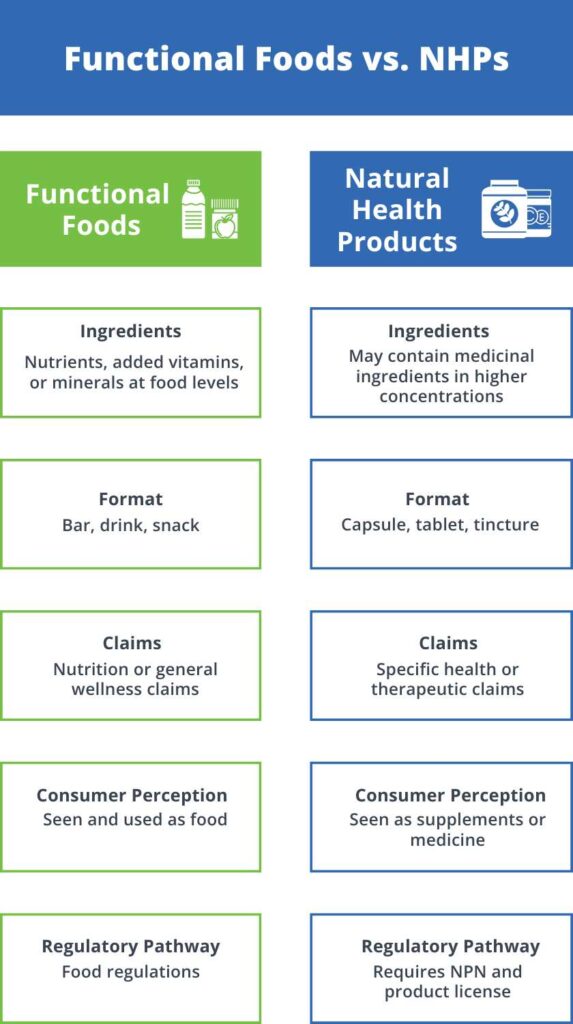
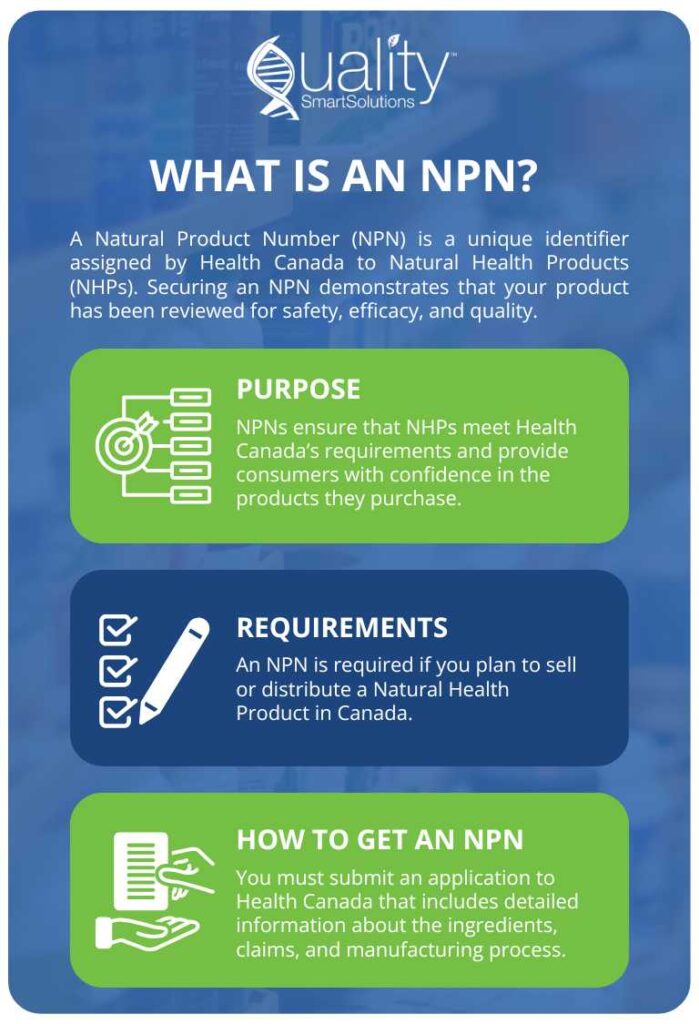
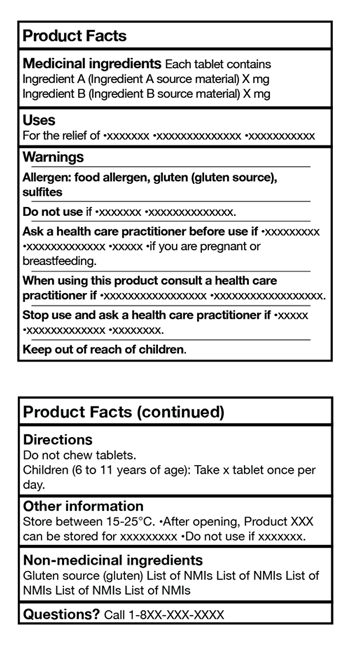
 Natural health products (NHPs) are widely used in Canada, ranging from vitamins, minerals, and herbal remedies to probiotics and homeopathic medicines. As these products play a vital role in promoting health and wellness, clear and accurate labeling is essential to ensure consumers can make informed decisions about the products they use.
Natural health products (NHPs) are widely used in Canada, ranging from vitamins, minerals, and herbal remedies to probiotics and homeopathic medicines. As these products play a vital role in promoting health and wellness, clear and accurate labeling is essential to ensure consumers can make informed decisions about the products they use.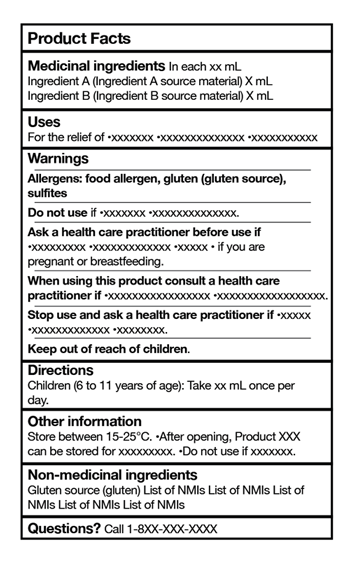
 6. Standardized Risk Information
6. Standardized Risk Information
 Implications for Manufacturers and Retailers
Implications for Manufacturers and Retailers

 Health Canada 2024 Changes for Nicotine Replacement Therapies (NRT)
Health Canada 2024 Changes for Nicotine Replacement Therapies (NRT) How to Create Health Canada Compliant Food Labels
How to Create Health Canada Compliant Food Labels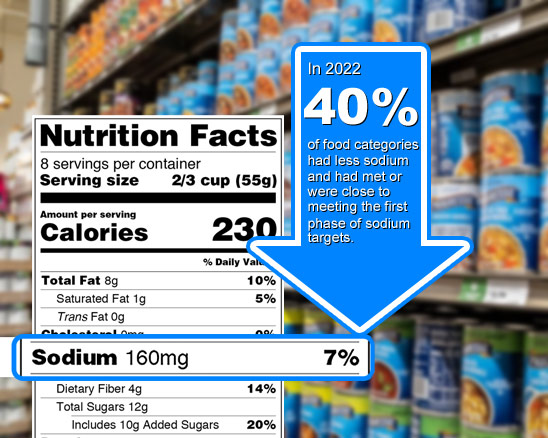

 This fall, Health Canada is anticipating sharing a policy consultation document about health products containing (CBD). This proposal has been in the works since 2019.
This fall, Health Canada is anticipating sharing a policy consultation document about health products containing (CBD). This proposal has been in the works since 2019.
 The Modernization of Cosmetics Regulation Act (MoCRA) brings significant changes for everyone in the cosmetics industry, from manufacturers to distributors. Its main goal is to make sure that cosmetic products are safe and comply with regulations before they reach consumers.
The Modernization of Cosmetics Regulation Act (MoCRA) brings significant changes for everyone in the cosmetics industry, from manufacturers to distributors. Its main goal is to make sure that cosmetic products are safe and comply with regulations before they reach consumers.
 Health Canada has unveiled its Forward Regulatory Plan for 2024-2026, outlining significant amendments to the Natural Health Products Regulations and the Food and Drug Regulations under the Food and Drugs Act.
Health Canada has unveiled its Forward Regulatory Plan for 2024-2026, outlining significant amendments to the Natural Health Products Regulations and the Food and Drug Regulations under the Food and Drugs Act. 
























 On September 20, 2023, Health Canada approved the use of L-alpha-glycerylphosphorylcholine (alpha GPC) as a supplement in foods. This decision followed a thorough safety review by Health Canada’s Food Directorate.
On September 20, 2023, Health Canada approved the use of L-alpha-glycerylphosphorylcholine (alpha GPC) as a supplement in foods. This decision followed a thorough safety review by Health Canada’s Food Directorate. This document is valuable for those interested in exploring the
This document is valuable for those interested in exploring the 



















 Introduction
Introduction
 Introduction: Navigating international trade regulations and the intricacies of Importer of Record (IOR) compliance and taxes can be complex. This comprehensive guide breaks down IOR compliance and its connection to tax obligations in the USA, offering a clear understanding for businesses engaged in global trade.
Introduction: Navigating international trade regulations and the intricacies of Importer of Record (IOR) compliance and taxes can be complex. This comprehensive guide breaks down IOR compliance and its connection to tax obligations in the USA, offering a clear understanding for businesses engaged in global trade.
 Food labels are more than just ingredient stickers on packaging; they are a key tool that helps consumers make informed choices about what they eat. This guide simplifies the complex world of food labeling regulations, focusing on the rules set by Health Canada, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and the European Union (EU). From required elements to health claims and country-of-origin labeling, this article breaks down the essential information you need to know about food labels and their purpose.
Food labels are more than just ingredient stickers on packaging; they are a key tool that helps consumers make informed choices about what they eat. This guide simplifies the complex world of food labeling regulations, focusing on the rules set by Health Canada, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and the European Union (EU). From required elements to health claims and country-of-origin labeling, this article breaks down the essential information you need to know about food labels and their purpose.
 Del Health Canada is a crucial regulatory body responsible for ensuring the safety and effectiveness of drugs and medical devices in Canada. This organization plays a vital role in protecting the health and well-being of Canadians by setting standards, conducting research, and enforcing regulations. In this guide, we’ll explore the responsibilities and functions of Del Health Canada in more detail.
Del Health Canada is a crucial regulatory body responsible for ensuring the safety and effectiveness of drugs and medical devices in Canada. This organization plays a vital role in protecting the health and well-being of Canadians by setting standards, conducting research, and enforcing regulations. In this guide, we’ll explore the responsibilities and functions of Del Health Canada in more detail.




